Eating Disorders, Obesity And Gut Microbiota
Source : Nutriactis/Rouen-Normandie hospital
Summary
- What is microbiota?
- Gut Dysbiosis
- Conclusion
What is microbiota?
Microbiota is the whole of non-pathogenic microorganisms (bacteria, viruses, parasites, fungi…) living in a specific environment. In our body, there are different microbiota from : gut, skin, mouth, vagina, lungs…The gut microbiota (GM) colonizes the entire digestive tract and is particularly rich in the small intestine and the colon (10 microorganisms).

Gut Dysbiosis
Gut dysbiosis is a change in the diversity and/or abundance of bacterial populations in the gut. This dysbiosis, observed in eating disorders (ED), appears to be a serious trail to explain and better understand some diseases, such as autoimmune diseases, inflammatory diseases or ED.Many factors, such as diet, stress, anxiety, sleep, can alter the GM and lead to dysbiosis.
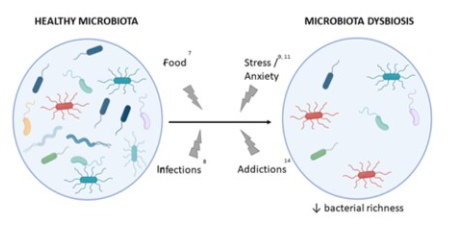
The gut microbiota in ED and obesity
In patients suffering from anorexia nervosa but also in obese patients, several studies highlight a dysbiosis with, in particular, a significant decrease in the bacterial diversity of the GM. This dysbiosis could contribute to the onset of ED and obesity; in particular by changing the production of hormones associated with food intake (hunger/satiety) and thus the eating behavior.
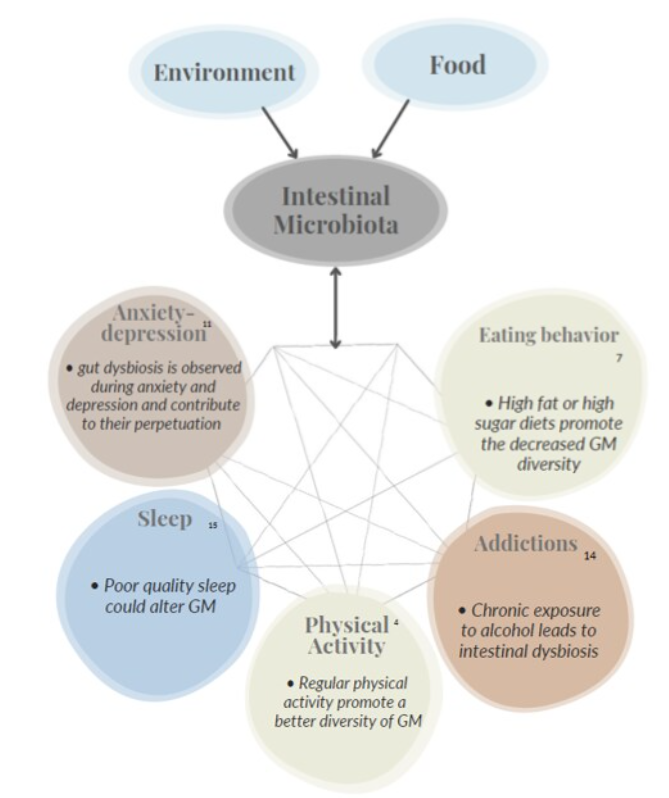
Conclusion
Diet has an impact on the composition of the gut microbiota, as well as stress, infections and addictions.
Knowing that gut dysbiosis has been observed in patients with ED or obesity, the study of the GM appears to be an interesting therapeutic strategie in the treatment of these pathologies.
Currently, many research focus on the development of probiotics (live microorganisms that exert beneficial effects on health) in order to re-shape the GM. Nutritional care is one of the key of ED and obesity care, and could also contribute to the re-shape of GM.
-
Download this article in PDF form
pdf – 843 KB