Associations Between EDs, Obesity and Social Networks
Source : Nutriactis/Rouen-Normandie hospital
Summary
- Introduction
- Some global figures in 2022
- The benefits and risks associated with the use of social networks
- What do we mean by addiction or problematic uses of SN?
- Associations between eating disorders, obesity and social networks
- Conclusion
Introduction
Social networks (SN) are the different digital platforms which are accessible via Internet and enable users to interact with each other, verbally and visually. Their purpose is the creation, sharing and viewing of social content among multiple users. There exists different types of social networks:
- Interactions and communications: Facebook, Twitter, Snapchat…
- Photo sharing: Instagram, Pinterest, Flickr…
- Video sharing: Youtube, Dailymotion, Tiktok, Twitch
- Romance and dating site: Meetic, Tinder, Adopte Un Mec …
- Job search and professional network: Linkedin, Viadeo, ryze…
- Messaging: Whatsapp, Messenger…
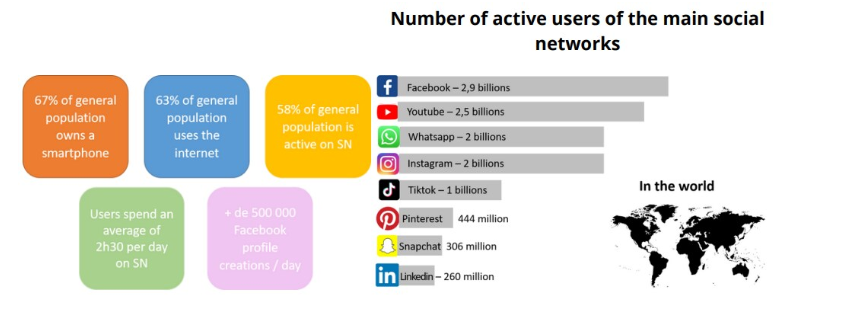
Some global figures in 2022
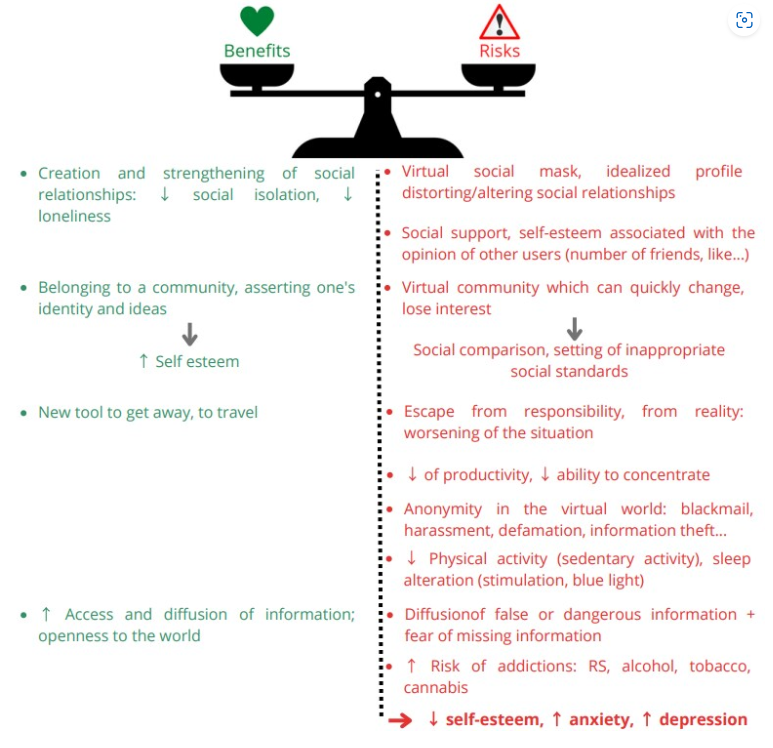
The benefits and risks associated with the use of social networks
What do we mean by addiction or problematic uses of SN?
There are many beneficial reasons for the increasing use of social networks. However, as the previous figure shows, for every benefit of social networks there may be a risk. This balance between the benefits and risks of social networks depends mainly on our use and behavioural attitude towards them. Although there is currently no consensus on the definition of addiction or problematic use of social networks, the scientific literature seems to define it as: a repetitive habit that is difficult to stop and that increases the risk of disease and/or is associated with personal or social problems. This problematic use or addiction is often associated with the notion of loss of control.
Associations between eating disorders, obesity and social networks
Problematic uses / addiction to SN can have many negative consequences, including on physical and mental health, such as:
→ Contributing to the diffusion of an ideal of thinness
Our society advocates an ideal of thinness via the diffusion of standardised silhouettes in which thinness is a systematic criterion. This repeated exposure to an ideal of thinness is reinforced with the onset of social networks and is often unrealistic, encouraging the development of an internalisation of thinness, i.e. the mental integration of a socially defined ideal of thinness which has a strong psychological and cognitive impact on the person.
→ Promoting lower self-esteem and increased anxiety
Scientific literature emphasizes that a strong internalization of thinness and social networks promotes a decrease in self-esteem and leads to an increase in body dissatisfaction, anxiety and depression.
→ Contributing to the onset of eating disorders
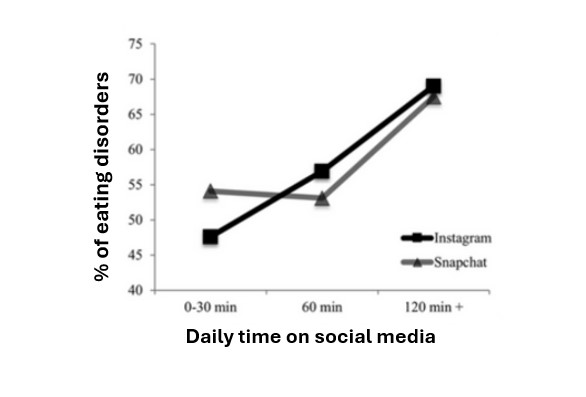
Beyond the internalisation of thinness, social networks can also promote inappropriate or even dangerous weight management behaviours. A literary study found a positive association between teenage girls’ Snapchat use and an increased likelihood of eating very little food according to strict plans, but also of skipping meals. Additionally, the Tumblr platform was associated with an increased risk of binge eating.
The use of social networks thus increases the risk of body concern and thus body dissatisfaction; with daily time on social networks being positively associated with the risk of eating disorders.
→ Increasing the risks of addictions
Additional literary studies have highlighted the impact of social networks on the increase in risk of addictions such as alcohol, tobacco or cannabis. Indeed, individuals who post alcohol-related photos are 2.34 times more likely to have excessive alcohol consumption, linked in particular to the normalisation of their addictive behaviour.
→ Altering physical activity and sleep patterns
- In adolescents, the use of social networks was associated with an increased likelihood of doing strict physical exercise or having physical hyperactivity or skipping meals in order to manage the weight [Wilksch, 2020]. On the contrary, time spent on social networks promotes sedentary behaviour, which contributes to the development of compulsive disorders and obesity.
- Changes in physical activity and prolonged exposure to screen light can also affect the quantity and quality of sleep.
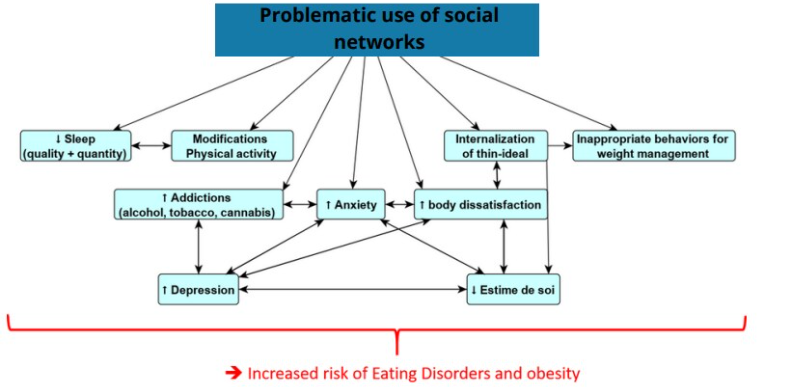
Conclusion
Problematic uses of social networks can therefore have significant adverse effects on physical and mental health. Many of these consequences are also risk factors for the onset of EDs and obesity and, as such, misuse of social networks can contribute to their onset.
And you, what about your use odf social networks:
- Which social network do you use most frequently?
- What is the average time you spend per day on social networks?
- Is your average time above or below the world average?
- Is your use of social networks having a negative impact on your life?