Link between body image perception, eating disorders and obesity
Source : Nutriactis/Rouen-Normandie hospital
Summary
- BODY DISSATISFACTION
- THE INTERNALIZATION OF THINNESS
- DYSMORPHOPHOBIA
Eating disorders and obesity are closely linked to body image perception, which is defined as the mental representation of one’s own body. The latter varies throughout life and can be influenced by feelings, socio-cultural context, entourage or media, but also by various phenomena such as the internalization of an ideal of thinness, dysmorphophobia or body dissatisfaction.
BODY DISSATISFACTION
- Body dissatisfaction is the perceived gap between the ideal body and the evaluation of own body. It is a subjective measure of self, directly linked to negative evaluations of body size, shape, musculature and weight, which can lead to dietary restriction. Through direct or indirect comments on appearance, social networks or family environment can exert a certain amount of
pressure towards beauty ideals and thus, body dissatisfaction. For some, restrictive dieting or intensive physical activity appear to be the only answers to this to this societal pressure; practices that can lead to serious long-term eating disorders. (see nutrition sheet; physical activity sheet).

THE INTERNALIZATION OF THINNESS

In today’s society, the internalization of thinness, characterized by the psychological / cognitive impact of a perceived and socially defined slimming ideal, is increasingly to models of thinness and the association between thinness and beauty. The complexity of achieving this thin ideal, conveyed by the media and social networks (retouched photos), partly justifies the impact of a strong internalization of thinness on body dissatisfaction and dysmorphophobia, as well as on self-esteem (cf. emotions). Therefore, over the longer term, strong internalization of thinness can lead to a change in eating behavior and an increased risk of developing EDs or obesity.
DYSMORPHOPHOBIA
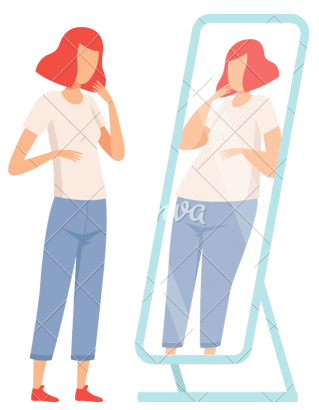
Dysmorphophobia is characterized by excessive thoughts and obsession with a very slight or even imaginary physical defect, whose perception of the person is completely disproportionate. It can cause suffering or major disruption to social, professional or school life and plays a role in the development of body dissatisfaction.
- Dysmorphophobia and either EDs or obesity are closely related disorders and frequently coexist, although the mechanisms involved are still poorly understood. Restrictive EDs are particularly affected by dysmorphophobia, with a vision of an overweight body even if their BMI is low. In compulsive EDs and obesity, binge eating is frequently accompanied by guilt and weight-control strategies (vomiting, laxatives, physical hyperactivity, etc.), reinforcing body dissatisfaction and promoting dysmorphophobia.
Body image perception therefore has a very strong influence on the onset and maintenance of EDs and obesity. Thus, reducing internalization of thinness, body dissatisfaction and dysmorphophobia must be an integral part of the management of EDs and obesity.