Why is water essential to human beings ?
Source : Nutriactis/Rouen-Normandie hospital
Summary
- The importance of water
- Recommendations
- Dehydration
- Tips to increase your water consumption
- Water consumption disorders and Eating Disorders (ED)
- Conclusion
Water is the most important constituent of the human body, accounting for around 60% of an adult’s body weight. Because of its multiple functions, it is essential to the survival of humans, who can only live for a few days without consuming water. The body starts to show the first signs of dehydration after only 24 hours without water intake
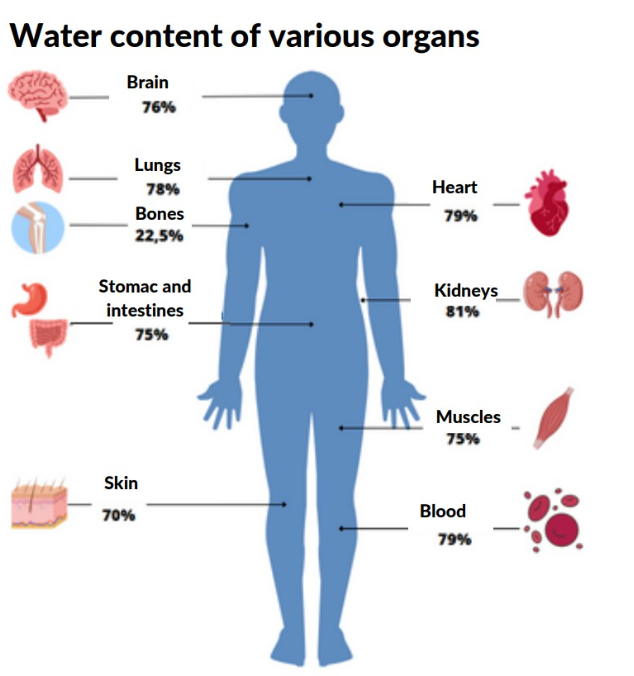
The importance of water
The body constantly eliminates water through breathing, sweating and excretions (urine, faeces).
Water consumption is essential to maintain intake above needs and thus keep the body healthy by:
- Being a main component of our cells and helping them function properly
- Participating in many of our body’s chemical reactions
- Transporting various molecules, such as nutrients, to the cells
- Enabling good blood circulation
- Helping to eliminate body waste (e.g. CO2 and toxins)
- Participating in the thermoregulation (maintenance of body temperature)
Recommendations

During the day, 2 to 2.5 liters of water are eliminated by the body, a loss that must be compensated in order to maintain the body’s equilibrium. It is recommended to drink at least 1.5 to 2 liters of water per day (for adults).
It is also recommended to drink even before feeling thirsty, especially for older adults, because their sensation of thirst is generally reduced.
However, the elimination of water by the body and therefore water requirements depend on many factors (temperature, age, physical activity…) and can therefore vary.

Dehydration
Dehydration is defined as the elimination of water and electrolytes by the body, which is not compensated by intake. Dehydration is usually caused by diarrhea, vomiting, heavy sweating, chronic illnesses such as diabetes, heavy use of diuretics (which increase urine production, such as coffee, tea or herbal infusions) or medication, but it may also be caused by not drinking enough water.
Symptoms of dehydration :
- Thirst, dry mouth
- Fatigue, exhaustion
- Dry skin, reduced skin elasticity
- ↓ of urine (and/or dark urine), ↓ sweating
- Reduced physical performance
- Headaches, dizziness, disorientation, faintness
- Disturbances in thermoregulation (hot/cold sensation)
- Behavioral changes (irritability, agitation…)
Dehydration may increase the risk of :
- Urinary tract infections
- Kidney stones
- Gallstones
- Constipation
- Cardiovascular diseases
- Hypertension
- Metabolic diseases such as diabetes
Tips to increase your water consumption
To increase your water consumption and reach the recommended levels, here are a few tips to help you:

Keep a water bottle with you and make sure it’s visible (e.g. on your desk)

Setup rituals: for example, drink a cup of water when you wake up in the morning, then a cup when you arrive at work, and one when you get home…

Flavour your water by adding : aromatic herbs(mint, basil…) or pieces of fruit ( strawberry, peach) … or vegetables (cucumber, tomato…)

Set reminders on your phone (e.g. every two hours)

Use an app or a connected watch to track your water consumption

Eat water rich foods (fruits and vegetables- except dried fruits)

Drink before you feel thirsty (still water, carbonated water)

Drink more soups (hot or cold)
Water consumption disorders and Eating Disorders (ED)
ED can be associated with changes in beverage consumption (increase or decrease) on a daily basis, known as water consumption disorders.
Potomania
- Potomania is characterized by the irrepressible and permanent need to drink large quantities of beverages, usually water (> 3L/day). Potomania induces an excessive water intake which will disrupte the normal body water balance (intake/elimination).
- People suffering from potomania can drink more than ten liters per day. Potomania is common in people suffering from ED, it can be used as a strategy to suppress hunger and feel more full. Sometimes, excessive water consumption is also used to induce compensatory behaviours (vomiting). Potomania is not without health risks: it can cause water retention, nausea and vomiting, headaches, electrolyte imbalance (disturbance of minerals in the body), kidney problems, cerebral edema (accumulation of fluids in the brain) and, in the most severe cases, death.
Water restriction
Unlike potomania, hydric restriction is characterized by insufficient or non-existent hydration. This water consumption disorder needs to be treated rapidly. If water intake is lower than the quantity of water eliminated by the body, there’s a risk of severe dehydration, which can lead to coma.
Conclusion

Water consumption is therefore essential to maintain a healthy body. It’s essential to listen to your body and to adapt your water intake to your needs, and therefore to the water eliminated by your body. For an healthy adult, it is recommended to drink a minimum of 1.5 to 2 liters of water per day.
-
Download this article in PDF form
pdf – 4 MB