Emulsifiers : What does the research say?
Source: BNP Paribas validated by the Rouen University Hospital
Summary
- Emulsifiers, what are they ?
- Few of the emulsifiers authorized in Europe and their uses
- How to identify emulsifiers in food products ?
- Emulsifiers and their impact on health
- Potential risks associated with the consumption of emulsifiers
Emulsifiers, what are they?
Emulsifiers are food additives that have the ability, due to a hydrophobic part (which repels water) and a hydrophilic part (which has affinity for water), to form a homogeneous mixture from substances thatnormally do not mix such as oil and water.
Emulsifiers are frequently used in the food industry to provide a uniform texture, stable over time andthus a more pleasant sensation in the mouth and a more appetizing appearance.
Diagram representing the role of emulsifiers:
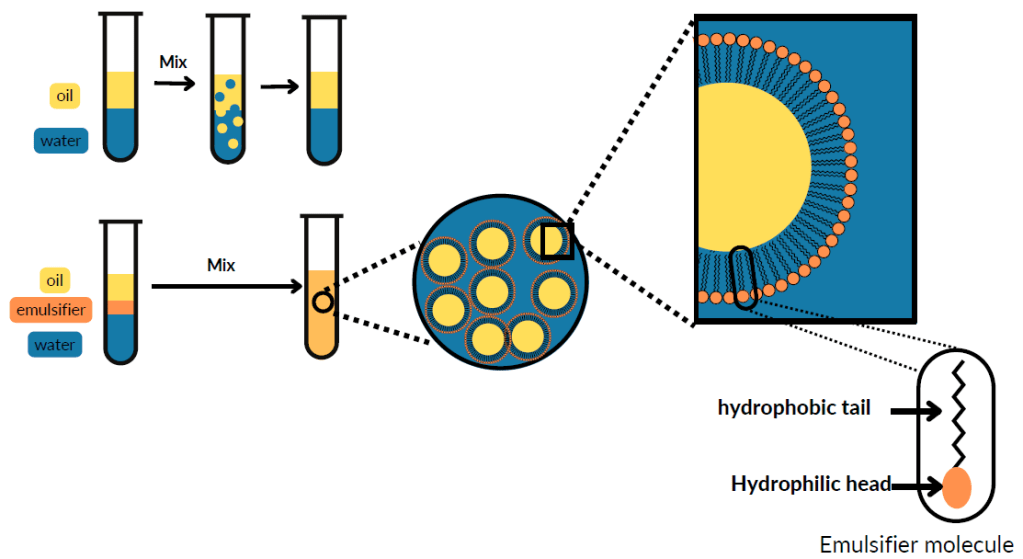
Emulsifiers are used to create an interface between two media (e.g. oiland water) to form a homogeneous mixture.
All food additives, including emulsifiers, are subject to a safety assessment by the European Food SafetyAuthority (EFSA) before being authorized in the European Union. Emulsifiers are present in almost all processed industrial products such as ready meals, ready-madesauces, chocolate, some dairy products, bread and many others.
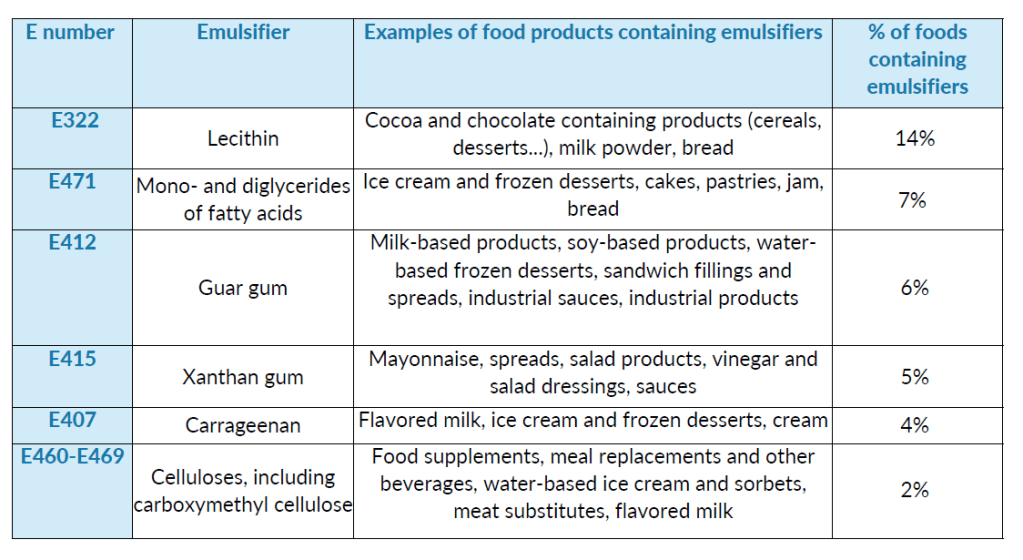
Few of the emulsifiers authorized in Europe and their uses
How to identify emulsifiers in food products?
According to EFSA regulations, each additive must be mentioned in the list of ingredients either by its name or by its identification number starting with E and must be preceded by its function (e.g.: emulsifier: E466 or emulsifier: carboxymethylcellulose). It is thus necessary to read carefully the labels to identify the presence of emulsifiers in the products that you buy or consume.

Emulsifiers and their impact on health
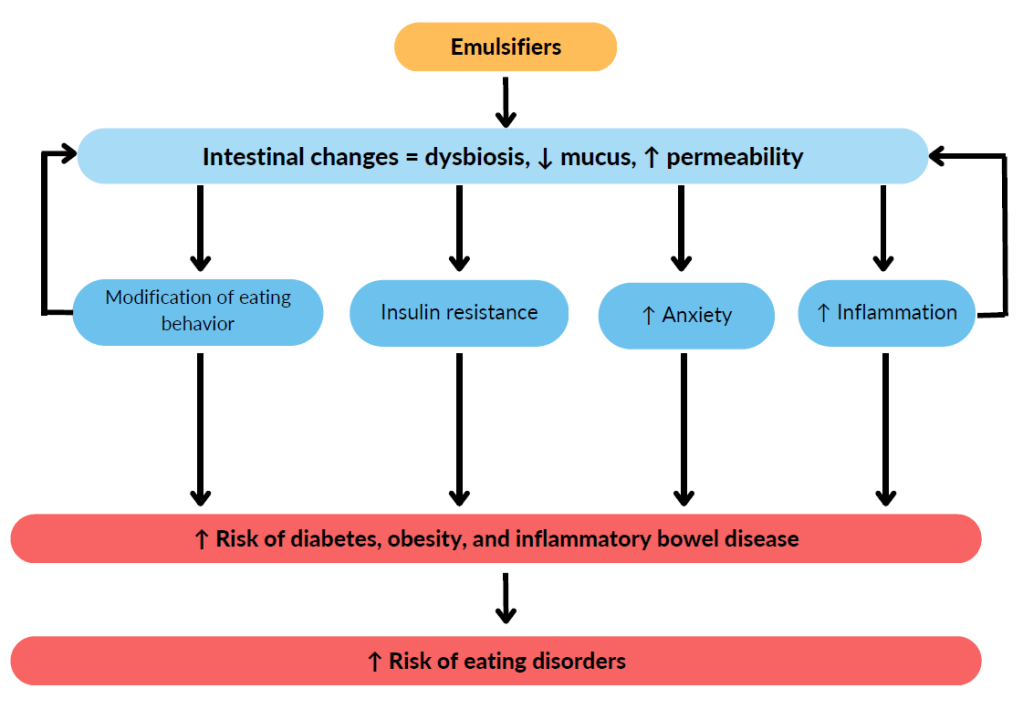
Studies on animals, but also studies on human microbiota have shown that many commonly used emulsifiers can modify the richness and diversity of the intestinal microbiota, leading to a dysbiosis. This dysbiosis can disturb the immune system by promoting the production of pro-inflammatory molecules and thus increasing the intestinal inflammation.
Animal studies have also shown that emulsifiers could increase intestinal permeability and decrease thethickness of the intestinal mucus (gel covering the cells of the intestine to protect them). These modifications could favor the penetration of pathogens (viruses, micro-organisms, toxic compounds…) into the host and thus increase the risck of intestinal inflammation and the développement of inflammatory bowel diseases.
Animal studies pointed out that disturbances of the intestinal microbiota induced by emulsifiers could also be associated with insulin resistance and increased food intake, leading to an increase in body weight and thus an increased risk of diabetes and obesity.
Another study describes an increase in anxiety-like behaviors and disturbances in social behaviors in mice consuming emulsifiers.
These studies question the safety of emulsifier consumption, but further studies, especially human studies, are needed to conclude.
The mechanisms describing the relationships between the consumption of emulsifiers, the microbiota, inflammation and various pathologies still need to be clarified.
Potential risks associated with the consumption of emulsifiers
Conclusion
The evidence for a direct link between emulsifiers and human disease is limited, however there are many potential mechanisms that may suggest their involvement in the dysbiosis of the gut microbiota and therefore in various diseases. Further studies are therefore needed to conclude on the impact of emulsifier consumption on human health.

-
Emulsifiers : What does the research say?
pdf – 5 MB
 You might be interested in these articles
You might be interested in these articles