Nutritional Education
Source : Nutriactis/Rouen-Normandie hospital
Summary
- The stakeholders in nutritional education
- Nutritional education strategies
- So why is nutrition education essential?
- Conclusion
A healthy and balanced diet combined with regular physical activity are essential for maintaining a healthy body. Nutritional education consists of a set of educational strategies designed to encourage beneficial, long-term eating habits and physical activity.
The stakeholders in nutritional education
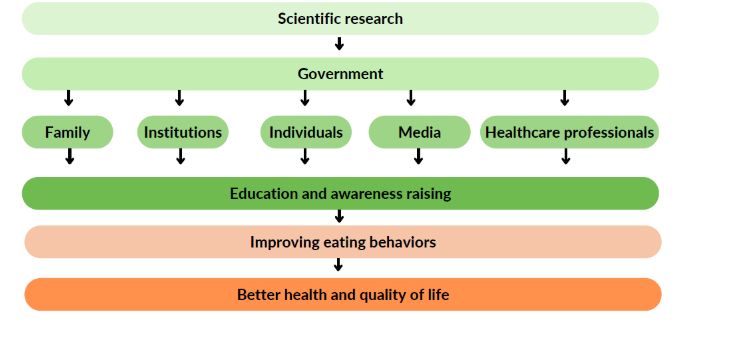
Eating behavior is influenced by a combination of individual factors (biological and personal) as well as social and environmental factors. Various actors can influence these factors through nutritional education.
1-Family
Studies have highlighted that healthy nutritional practices during the first 1,000 days of life have a positive impact on a child’s future health and eating behavior. Additionally, parents’ eating habits strongly influence those of their child, which are generally perpetuated throughout their life. Therefore, family nutritional education is necessary and should be carried out from an early age by both parents.
2- Institutions
a- School
Nutritional education through school has proven effective in improving children’s knowledge, attitudes, and practices. Children and adolescents spend most of their time at school, and their behaviors are thus partly influenced by the school environment, making it an appropriate setting for implementing nutritional education. This aims to contribute to children’s health and well-being by promoting healthy eating and appropriate physical activity. Studies show that children’s participation in nutritional intervention programs leads to healthier food choices and a reduction in overweight and obesity. Furthermore, after these intervention programs, children generally engage in physical activity more frequently.
b-Workplace
Workplaces are suitable to promoting physical activity and healthy eating. They offer a favorable context for nutritional education because they are attended by all employees, most of whom have one or more meals there. Therefore, nutritional education at work can impact a large number of people, including those who are less inclined to change their habits without support. Several studies have highlighted that nutritional interventions in the workplace could improve well-being, help prevent certain chronic diseases, reduce absenteeism, and improve productivity.
3-Healthcare professionals
The dietitian’s role is to adapt everyone’s diet to meet their nutritional needs and to provide advice tailored to each individual’s eating behaviors and habits. Therefore, they are an essential player in nutritional education. In case of difficulties with one’s eating behaviors or weight, the general practitioner is generally the first point of contact. They can then refer the patient to a nutritionist or any other specialized healthcare professional as needed.
4- Government
Nutrition policy is defined as a set of actions initiated by the government to preserve the health of the population by providing them with scientifically validated and essential information for proper nutritional education. Public authorities therefore play an important role in disseminating nutritional information to the population, making them a key player in nutritional education.
5- Individuals
Nutritional education aims to inform individuals in order to enhance their ability to modify or adopt nutritional behaviors that are beneficial to their health and well-being. For sustainable and effective change, the individual must be an active participant in their nutritional education and thus in their health. For this, motivation and personal commitment are essential.
Nutritional education strategies
1- Family
Parents can implement a number of strategies to help their children adopt healthy eating habits:

That’s why it’s important for everyone to know what a healthy diet is and how to implement it, without forgetting the pleasure of eating that is an integral part of a balanced diet.
2- Institutions
a- Schools
- Several nutrition education strategies can be used in schools: first of all, integrating nutrition education into the classroom with theoretical lessons on the importance of healthy eating and physical activity, and how to implement them. Studies emphasize that putting into practice the nutritional knowledge learned through activities such aschallenges or cooking workshops, is a highly effective educational strategy. These activities enable the child to better assimilate the information acquired. Organizing awareness days can also be an effective strategy for educating children. Meals at school are very important and are also good teaching tools. Children can discover and taste different foods and therefore different flavors. This diversity of flavors enables them to discover and maintain the pleasure of eating that is also essential to a balanced diet.
- In France, the Education Code requires that information and education on food and food waste be provided in schools, but this is not the case in all countries. For example, Finland is a country with a high level of nutritional education in schools; students aged between 15 and 16 have three lessons a week, during which they learn how to cook and the benefits of a proper nutrition. Latin American countries, on the other hand, do not generally integrate nutrition education into their schools.
b- Workplace
Several actions can be initiated within a company by senior management in collaboration with occupational medicine, communication departments, employees and even outside contributors to share nutrition related information. The strategies used depend on each company and can be :

3- Healthcare professionals
There are several ways in which healthcare professionals can spread nutritional knowledge:
- Consultation
- In group therap
- Publishing scientific studies
- Publishing documentation for the general public
- In collaboration with companies, schools, etc.
4- The government
France has implemented a public health nutrition policy, by developing the Programme National Nutrition Santé (PNNS) to promote healthy eating and physical activity, and raise awareness of health risk factors. The PNNS establishes nutritional recommendations for the general population to meet objectives drawn up by expert committees. For example, one ofthe objectives is “to increase the consumption of fruit and vegetables among adults, so that at least 80% of the population consume at least 3.5 portions of fruit and vegetables a day, and at least 55% consume at least 5 portions of fruit and vegetables a day”. It is with this objective in mind that the “Eat at least 5 portions of fruit and vegetables a day” message is being disseminated.
The success of the PNNS is based on the mobilization of a wide range of players in society, thanks to the provision of tools and support to encourage everyone to get involved:
- The “Entreprises actives du PNNS” and “Établissements actifs du PNNS” charters reward companies that develop actions to improve the nutrition of their staff, and provide them with support to help them implement nutritional strategies.
- In schools, in addition to the education code (mentioned above), a wide range of materials are made available to the various players within schools, to help them disseminate information more easily.
- Public authorities also play a role in disseminating nutritional information to the general population via a variety of channels:
- Public websites that disseminate the PNNS recommendations, such as mangerbouger.fr
- -The media (social media, TV ads,…) play an important role in disseminating key nutritional messages: “Avoid eating foods that are too fatty, too sweet or too salty”.
- –Packaging of food products in part due to the Nutri-Score. The Nutri-Sc ore is a logo
found on packaging that provides information on the nutritional quality of products in a simplified form, with a scale of colors associated with letters ranging from A (most favorable) to E (least favorable). It makes it easier for consumers to understand nutritional information, helping them make informed choices.
Taxes on certain food products are also imposed by various governments. For instance, these taxes generally apply to products with added sugar. In France, there are taxes on non-alcoholic beverages containing added sugars (sodas, fruit juices, etc.) or synthetic sweeteners (“light” drinks) to encourage manufacturers to add less sugar to their products.
Scientific studies are the foundations of nutritional knowledge, which needs to be popularized and disseminated to the general public, and are at the origin of initiatives by stakeholders and political decision-makers. Public authorities also support scientific research and thus the production of scientific knowledge in nutrition.
Specific nutritional education is provided in anumber of different contexts, in particular for chronic diseases such as diabetes, obesity and liver disease, as well as for pregnant and breast-feeding women. However, nutrition education needs to be perfected for prevention in the general population.
So why is nutrition education essential?
Eating behavior (choices, habits, food sensations, etc.) can influence health, and in particular the onset of certain pathologies, which is why nutritional education is essential. It enables :
- Governments to achieve a healthier population with a better quality of life.
- Institutions to improve the health of their students/employees by educating them and offering them a healthy diet.
- Families to acquire new knowledge that will improve their current and future health, and strengthen family ties by encouraging healthy food preparation.
- Individuals to understand their nutritional needs, enjoy eating healthy foods and improve their health.
Conclusion
Indeed, balanced eating habits and physical activity reduce the risk of health problems. This is why nutritional education is an important foundation for healthy living, and should be introduced from an early age.
-
Download the pdf version here
pdf – 2 MB
 You might be interested in these articles
You might be interested in these articles